目的
基于国密设计一个简易的密钥协商协议;
分析
SM2算法原理
SM2算法是国家密码管理局于2010年12月17日发布的椭圆曲线公钥密码算法,是ECC(Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem)算法的一种,基于椭圆曲线离散对数问题,计算复杂度是指数级,求解难度较大,同等安全程度要求下,椭圆曲线密码较其他公钥算法所需密钥长度小很多。与RSA算法相比,SM2算法是一种更先进安全的算法。在我们国家商用密码体系中SM2算法被用来替换RSA算法。SM算法作为一种ECC算法,其原理如下:
- 用户A选定一条合适加密的椭圆曲线
,如: ,并取椭圆曲线上一点,作为基点G; - 用户A选择一个私有密钥k,并生成公钥
: ; - 用户A将
和点(公钥) 传给用户B; - 用户B接到信息后 ,将待传输的明文M编码到
上一点M,并产生一个随机整数 ,加密开始; - 用户B计算点
, ; - 用户B将
、 传给用户A; - 用户A接到信息后,计算
,再对点M进行解码就可以得到明文;
密码学中,描述一条
- p越大越安全,但越大,计算速度会变慢,200位左右可以满足一般安全要求;
; ; ; - n 为素数;
- h≤4;
SM2程序编写
SM2.java分析- 首先从
ecc_param中获取参数对赋值,来确定一条椭圆曲线 ecc_curve; - 同时获取
的值,得到基点G; - 然后实例化一个
ECKeyGenerationParameters对象来得到密钥生成器的相关参数; - 最后实例化一个
ECKeyPairGenerator对象生成密钥对;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public SM2() {
this.ecc_p = new BigInteger(ecc_param[0], 16);
this.ecc_a = new BigInteger(ecc_param[1], 16);
this.ecc_b = new BigInteger(ecc_param[2], 16);
this.ecc_n = new BigInteger(ecc_param[3], 16);
this.ecc_gx = new BigInteger(ecc_param[4], 16);
this.ecc_gy = new BigInteger(ecc_param[5], 16);
this.ecc_w = 127;
this.ecc_gx_fieldelement = new Fp(this.ecc_p, this.ecc_gx);
this.ecc_gy_fieldelement = new Fp(this.ecc_p, this.ecc_gy);
this.ecc_curve = new ECCurve.Fp(this.ecc_p, this.ecc_a, this.ecc_b);
this.ecc_point_g = new ECPoint.Fp(this.ecc_curve, this.ecc_gx_fieldelement, this.ecc_gy_fieldelement);
this.ecc_bc_spec = new ECDomainParameters(this.ecc_curve, this.ecc_point_g, this.ecc_n);
ECKeyGenerationParameters ecc_ecgenparam;
ecc_ecgenparam = new ECKeyGenerationParameters(this.ecc_bc_spec, new SecureRandom());
this.ecc_key_pair_generator = new ECKeyPairGenerator();
this.ecc_key_pair_generator.init(ecc_ecgenparam);
}- 首先从
SM2算法加解密分析SM2Utils.java
对明文M加密
流程如下,其中由于
,第3步计算 忽略 
详细代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19//加密
public static String encrypt(byte[] publicKey, byte[] data) throws IOException {
if (publicKey == null || publicKey.length == 0) {
return null;
}
if (data == null || data.length == 0) {
return null;
}
byte[] source = new byte[data.length];
System.arraycopy(data, 0, source, 0, data.length);
Cipher cipher = new Cipher();
SM2 sm2 = SM2.Instance();
ECPoint userKey = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(publicKey);
ECPoint c1 = cipher.Init_enc(sm2, userKey);
cipher.Encrypt(source);
byte[] c3 = new byte[32];
cipher.Dofinal(c3);
return Util.byteToHex(c1.getEncoded()) + Util.byteToHex(source) + Util.byteToHex(c3);
}对密文C解密
流程如下,其中由于
,第2步计算 忽略 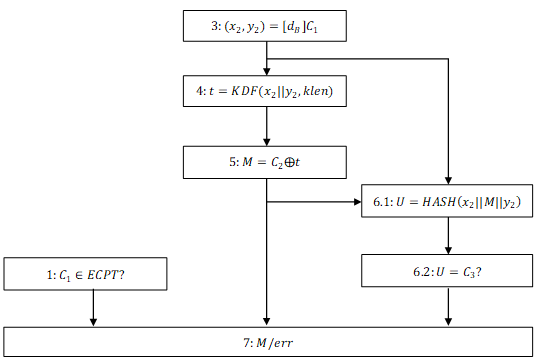
详细代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29//解密
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] privateKey, byte[] encryptedData) throws IOException {
if (privateKey == null || privateKey.length == 0) {
return null;
}
if (encryptedData == null || encryptedData.length == 0) {
return null;
}
//加密字节数组转换为十六进制的字符串,长度变为encryptedData.length*2
String data = Util.byteToHex(encryptedData);
/*分解加密字串
* (C1 = C1标志位2位 + C1实体部分128位 = 130)
* (C3 = C3实体部分64位 = 64)
* (C2 = encryptedData.length * 2 - C1长度 - C2长度)
*/
byte[] c1Bytes = Util.hexToByte(data.substring(0,130));
int c2Len = encryptedData.length-97;
byte[] c2 = Util.hexToByte(data.substring(130,130+2*c2Len));
byte[] c3 = Util.hexToByte(data.substring(130+2*c2Len,194+2*c2Len));
SM2 sm2 = SM2.Instance();
BigInteger userD = new BigInteger(1, privateKey);
//通过C1实体字节来生成ECPoint
ECPoint c1 = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(c1Bytes);
Cipher cipher = new Cipher();
cipher.Init_dec(userD, c1);
cipher.Decrypt(c2);
cipher.Dofinal(c3);
return c2;
}测试SM2算法
测试代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
//生成密钥对
generateKeyPair();
String message = "leeyuxun@163.com";
byte[] sourceData = message.getBytes();
System.out.println("明文消息: ");
System.out.println(message);
//下面的秘钥可以使用generateKeyPair()生成的秘钥内容
// 国密规范正式私钥
String prik = "3690655E33D5EA3D9A4AE1A1ADD766FDEA045CDEAA43A9206FB8C430CEFE0D94";
// 国密规范正式公钥
String pubk = "04F6E0C3345AE42B51E06BF50B98834988D54EBC7460FE135A48171BC0629EAE205EEDE253A530608178A98F1E19BB737302813BA39ED3FA3C51639D7A20C7391A";
System.out.println("密文: ");
String cipherText = SM2Utils.encrypt(Util.hexToByte(pubk), sourceData);
System.out.println(cipherText);
System.out.println("解密: ");
String plainText = new String(SM2Utils.decrypt(Util.hexToByte(prik), Util.hexToByte(cipherText)));
System.out.println(plainText);
}运行结果如下,SM2可以进行正确加解密;
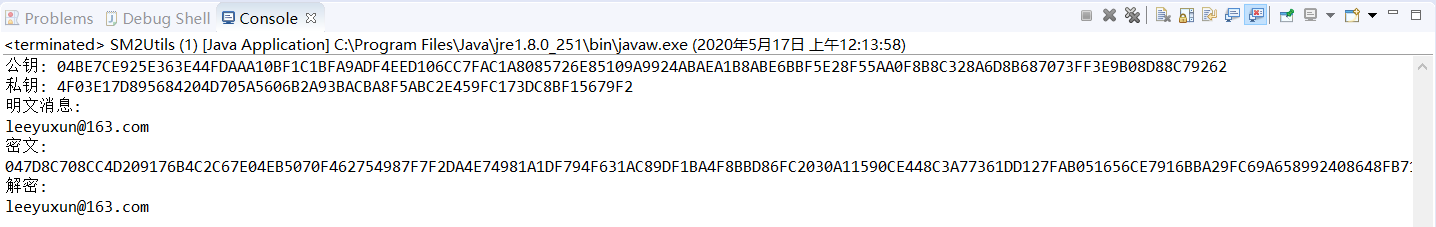
- SM2算法的实现关键点是保证加密流程第4步计算的
与解密流程第3步计算的 相等:由于解密流程第3步计算 的结果 是加密流程第4步计算值,所以加密流程第4步计算的 与解密流程第3步计算的 相等。
SM3摘要算法
SM3是国家密码管理局于2010年12月17日发布的一种密码散列函数标准。在商用密码体系中,SM3主要用于数字签名及验证、消息认证码生成及验证、随机数生成等,其算法公开。据国家密码管理局表示,其安全性及效率与SHA-256相当。SM3核心代码如下:
1 | public static void main(String[] args) |

密钥协商设计
协商过程如下:
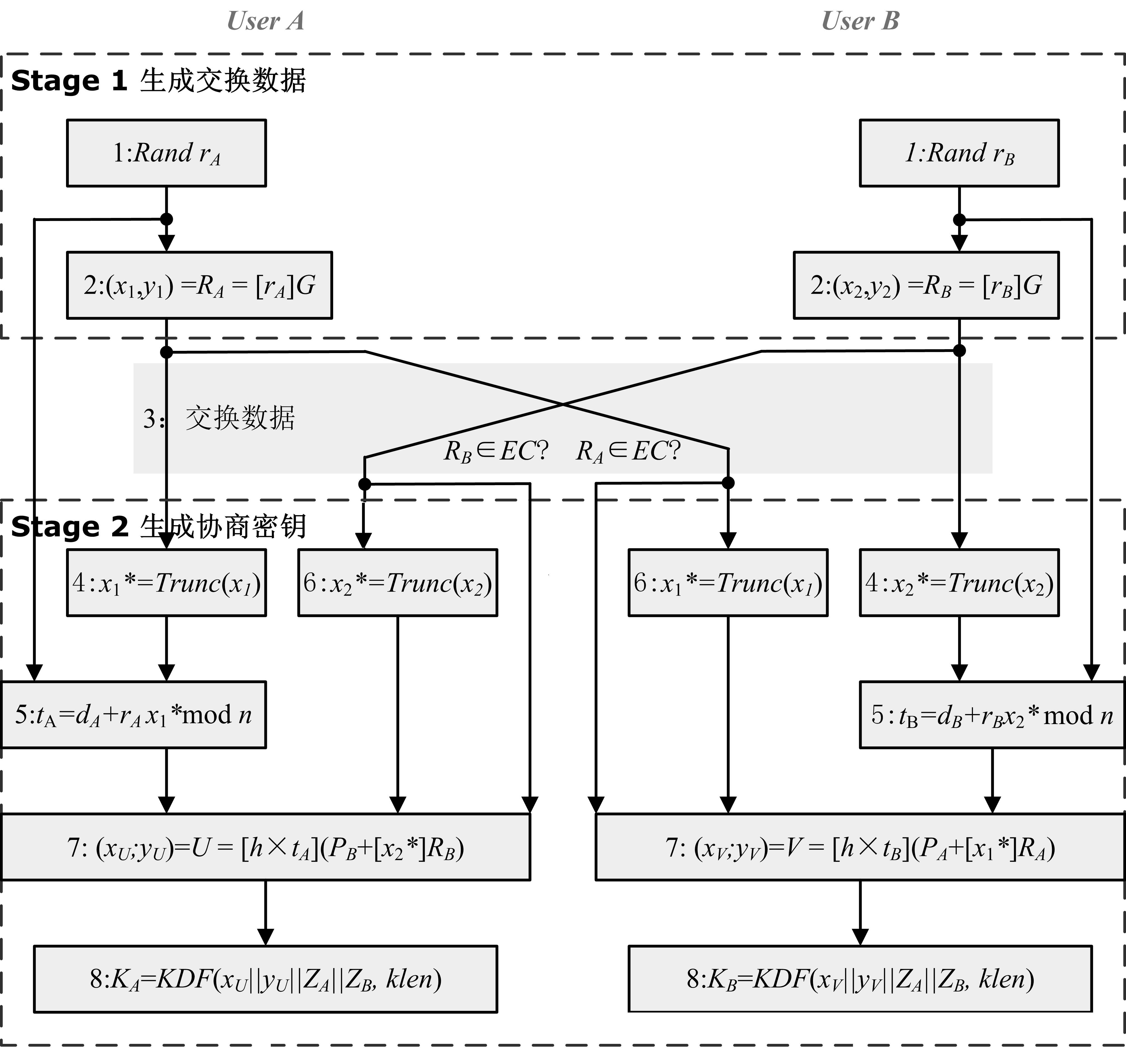
结合具体的代码来解释上述协商过程。由于使用到socket进行双方的交互,设定Socket Client为User A,Socket Server为User B;
Client向Server发起连接请求,后实例化一个SM2_Exchange对象A,得到其公私钥,并计算A的身份标识
,接着实例化一个Exch对象,并使用A的私钥初始化,产生一个随机数r充当临时私钥,得到 ; 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 23333;
//和server建立连接
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);
System.out.println("client is working...");
SM2_Exchange A = new SM2_Exchange();
A.generateKeyPair();//
byte[] pubK_A = A.getPubKey();//获得A的公钥
byte[] priK_A = A.getPriKey();//获得A的私钥
byte[] ZA =new byte[32];
A.computeZ("A is a client",ZA);
Exch A_EX = new Exch();
A_EX.Init(priK_A);
ECPoint R_A = A_EX.R1;//获得RA
byte []RA = R_A.getEncoded();同时Server端接受Client发起的Socket连接后,进行与Client端进行相同的操作,得到
; 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15int port = 23333;
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);
// 服务器端监听
System.out.println("server is waiting...");
Socket socket = server.accept();
SM2_Exchange B = new SM2_Exchange();
B.generateKeyPair();
byte[] pubK_B = B.getPubKey();//获得B的公钥
byte[] priK_B = B.getPriKey();//获得B的私钥
byte[] ZB =new byte[32];
B.computeZ("B is a server",ZB);
Exch B_EX = new Exch();
B_EX.Init(priK_B);
ECPoint R_B = B_EX.R1;//获得RB
byte[] RB = R_B.getEncoded();其中Exch对象初始化的代码如下,参数为私钥,计算
的同时计算出 和 的值; 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public void Init(byte[] priKey)
{
SM2 sm2 = SM2.Instance();
w= sm2.ecc_w;
AsymmetricCipherKeyPair key = sm2.ecc_key_pair_generator.generateKeyPair();
ECPrivateKeyParameters ecpriv = (ECPrivateKeyParameters) key.getPrivate();
ECPublicKeyParameters ecpub = (ECPublicKeyParameters) key.getPublic();
BigInteger r = ecpriv.getD(); //随机数r,在这是用临时私钥代替
R1 = ecpub.getQ(); //临时私钥对应的临时公钥,也就是R1
BigInteger x1 = R1.getX().toBigInteger();//取出R1的横坐标x1
BigInteger x_1 = computeX(w,x1);
compute_t(priKey,x_1,r);//计算t
}接下来A需要初始化一个Negotiation对象,即需要发送给B的交换数据包括
以及A的身份 ,然后利用ObjectOutputStream发送给B,并接收从B发来的Negotiation对象,解析后利用 计算出共享密钥; 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14OutputStream agree = socket.getOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream negot = new ObjectOutputStream(agree);
negot.writeObject(new Negotiation(pubK_A,RA,ZA));
negot.flush();
InputStream fromB = socket.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream isfromB = new ObjectInputStream(fromB);
Object obj = isfromB.readObject();
Negotiation B = (Negotiation) obj;
SM2 sm2 = new SM2();
ECPoint pubB = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(B.getpub());
ECPoint R_B = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(B.getR());
byte [] ZB = B.getZ();
String sharedkey= A_EX.computeKey(pubB,R_B,ZA,ZB);B接收到A发来的Negotiation对象解析后,利用
计算出共享密钥,然后发送自己的Negotiation对象给A; 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14InputStream fromA = socket.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream isfromA = new ObjectInputStream(fromA);
Object obj = isfromA.readObject();
Negotiation A = (Negotiation)obj;
SM2 sm2 = new SM2();
ECPoint pubA = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(A.getpub());
ECPoint R_A = sm2.ecc_curve.decodePoint(A.getR());
byte [] ZA = A.getZ();
String sharedkey = B_EX.computeKey(pubA,R_A,ZA,ZB);
OutputStream agree = socket.getOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream negot = new ObjectOutputStream(agree);
negot.writeObject(new Negotiation(pubK_B,RB,ZB));
negot.flush();其中Negotiation类的如下,需要进行Socket传输,继承了一个序列化接口;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23import java.io.Serializable;
public class Negotiation implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private byte[] pub;
private byte[] R_;
private byte[] Z_;
public Negotiation(){
}
public Negotiation (byte[] pub, byte [] R_, byte[] Z_) {
this.pub = pub;
this.R_ = R_;
this.Z_ = Z_;
}
public byte[] getpub() {
return pub;
}
public byte[] getR() {
return R_;
}
public byte[] getZ() {
return Z_;
}
}计算共享密钥的computeKey方法如下:
获得
; 计算出U的纵横坐标;
利用KDF来生成256比特公钥;
由于A、B接下来使用SM4进行对称加解密,所以暂时只取前128位作为公钥;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public String computeKey(ECPoint pubKey_B,ECPoint RB,byte[] Z1,byte[] Z2) {
BigInteger x2 = RB.getX().toBigInteger();//取出RB的横坐标x2
BigInteger x_2 = computeX(w,x2);
ECPoint U = computePoint(x_2,pubKey_B,RB);
//取出U的横坐标ux,为字节数组
ux = Util.byteConvert32Bytes(U.getX().toBigInteger());
//取出U的横坐标uy,为字节数组
uy = Util.byteConvert32Bytes(U.getY().toBigInteger());
//用于存储KDF产生的256比特共享密钥
byte[] key = new byte[32];
//计算共享密钥
KDF(key,Z1,Z2);
//用于存储前128位共享密钥
byte[] result = new byte[8];
System.arraycopy(key,0,result,0,result.length);
//将公钥从字节数组转换为16进制字符串,输出公钥
System.out.print("public key:");
//将公钥从字节数组转换为16进制字符串,输出公钥
System.out.println(Util.getHexString(result,true));
return Util.getHexString(result,true);
}AB双方都得到公钥后,A尝试使用SM4算法采用ECB模式加密一条消息发送给B;
1
2
3
4
5OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
String message = "leeyuxun@163.com";
SM4Utils sm4 = new SM4Utils();
sm4.setSecretKey(sharedkey.toString());
sm4.setHexString(false);B收到A发来的密文,尝试用共享密钥利用SM4算法进行解密;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
StringBuilder enmessage = new StringBuilder();
inputStream.toString();
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//只有当客户端关闭它的输出流的时候,服务端才能取得结尾的-1
enmessage.append(new String(bytes, 0, len, "UTF-8"));
}
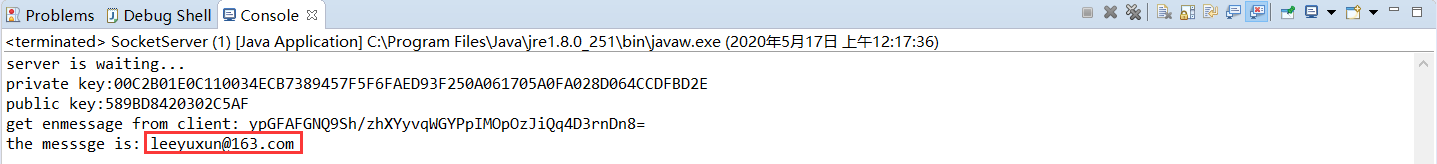
System.out.println("get enmessage from client: " + enmessage);
SM4Utils sm4 = new SM4Utils();
sm4.setSecretKey(sharedkey.toString());
sm4.setHexString(false);
String plainText = sm4.decryptData_ECB(enmessage.toString());
System.out.println("the messsge is: " + plainText);
程序运行结果
client(User A)运行结果:
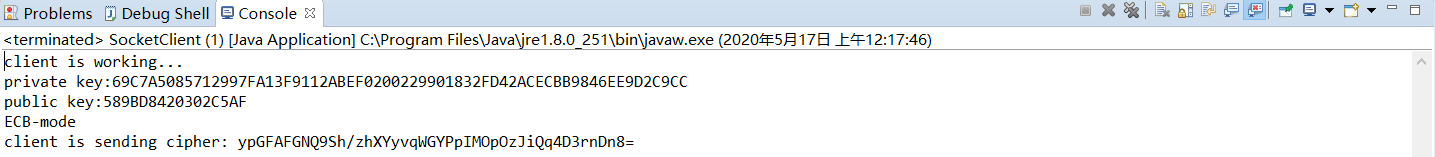
server(User B)运行结果: